Table of Contents
Mild steel (also know as plain-carbon steel or low-carbon steel, something we’ll go over later in the article) is iron that contains small percentage of iron, which makes it strong but not readily tempered. But, we will elaborate on this a bit more throughout the remainder of the article.
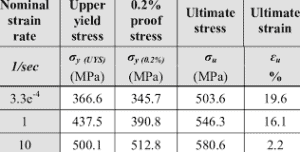
Properties of Mild Steel / Low Carbon Steel
Mild steel is known for being low in carbon (hence the name Low-Carbon Steel) and tends to be cheaper and easier to make. The carbon content that you’ll typically find in a piece of Mild Steel will typically range from .05% to .30% depending on the weight which makes it ductile. On the other hand, high carbon steel will typically have a carbon count of .3% 2%. If the steel has a higher carbon count than that it would have to be called cast iron. Mild steel is not counted as an alloy which means that one won’t find many other alloys included in it’s makeup.
*you can improve the surface hardness of mild steel via carburizing
Due to the fact that Mild Steel has a lower carbon count it is known as being more weldable, and machinable that higher carbon steels.
*The carbon content that you’ll typically find in a piece of Mild Steel will typically range from .05% to .30% depending on the weight which makes it ductile.
It also means, however, that it is almost impossible to harden and make stronger through quenching and heating. The lower carbon count also means that it has less tensile strength than both alloy and higher carbon steels. Also take note of the fact that Mild Steel has a vast amount of ferrite and iron, which makes it magnetic.
*Ferrite is a solid solution phase of carbon that’s dissolved in alpha-iron, which is a body-centered cubic crystal (You can learn more about body centered cubic crystals here)
Not having alloying materials in it’s makeup means that improperly coating mild steel will result in the appearance of rust. The great thing about mild steel not having alloying materials is that it is incredibly affordable. The price of mild steel as well as it’s other characteristics is a major contributing factor to its popularity among welders.
How exactly do they make Mild Steel?
The process of making Mild Steel isn’t that much different from the process of making other carbon steels. For the most part, it’s made with both iron ore and coal. After the materials are taken from the ground they are blended together using a blast furnace. After the initial melting, they are moved to another furnace to get rid of any impurities in the combination as well as make the necessary adjustments to the mild steel chemical makeup. After the melting is finished the mild steel cools and is molded into a rectangular shape. Using both hot rolling and cold drawing the rectangular mild steel is brought down to the necessary size.
What is Mild Steel used for?
Below are a few of the basic applications of Mild Steel:
- Signs
- Structural Steel:
- Vehicles
- Furniture
- Wire
- Decorations
- Nails
- Fencing